Abstract
Introduction
B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) is a cell surface receptor highly and selectively expressed on normal plasma cells and transformed plasma cells in multiple myeloma (MM) patients. Upon ligand binding, BCMA initiates signals that promote the survival of MM cells and the production of immunosuppressive factors. Therapeutics that target BCMA are being investigated in the clinic, with encouraging preliminary results. HPN217 is a Tri-specific T Cell-Activating Construct (TriTAC) specific to BCMA, to serum albumin for half-life extension, and to CD3ε for redirecting T cells against MM cells. It is currently being evaluated in a phase 1 /2 clinical trial for relapsed or refractory MM (NCT04184050). Herein, we describe translational studies to examine factors that may impact the therapeutic efficacy of HPN217, including the target BCMA, in membrane-bound or soluble form, and concomitant or combination therapeutics such as γ-secretase inhibitor (GSI) and dexamethasone.
Results
To evaluate the effects of HPN217 against primary MM cells, we used a patient-derived 3D-culture system (3DTEBM) designed to recapitulate the biology within the bone marrow microenvironment. 3DTEBM seeded with bone marrow accessory cells and autologous plasma recreate niches along an oxygen gradient that enable the survival and expansion of autologous MM cells without additional nutrient supplements. 3DTEBM's were established from 5 MM patients with varying ratios of autologous CD3+ T cells to MM cells (0.15-0.6). Although the functional competence of the T cells was unknown, HPN217 was able to mediate MM cell killing in 80% of the cultures with up to 71% of MM cells eliminated at a T cell/MM cell ratio of 0.45. The anti-tumor efficacy of HPN217 correlated strongly (R 2 = 0.99) with BCMA expression on the MM cells as measured by flow cytometry, suggesting the number of target receptors can be a limiting factor in efficacy. Consistent with this result, pre-incubation of target cells with 1 or 10 μg/mL anti-BCMA reduced the activity of HPN217 in T cell-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (TDCC) assays using healthy donor T cells and MM cell lines.
Soluble BCMA (sBCMA) is produced when the extracellular domain of BCMA is cleaved by γ-secretase. It may act as a sink for HPN217. There was no correlation between the activity of HPN217 and the quantity of sBCMA in 3DTEBM. However, in TDCC assays, the addition of 6.25, 25 and 100 nM recombinant BCMA respectively led to 4-, 9- and 28-fold increases in the EC 50 of HPN217. Taken together, these data underscore the importance of preserving BCMA on MM cells and reducing sBCMA in circulation. Interestingly, treatment of MM cell line RPMI8226 with the GSI LY-3039478 for 24 hours increased the cell surface expression of BCMA by 3.6 folds. Using RPMI8226 as target cells in the 3DTEBM system, LY-3039478 increased the killing efficacy of HPN217-redirected primary T cells by 1.9 folds.
Dexamethasone (Dex) is used with other therapeutics for treating MM. It is also commonly given to manage cytokine release syndrome (CRS) caused by T cell engagers. We conducted TDCC assays in the presence of 0.07-300 nM Dex to simulate plasma concentrations relevant to dose levels of Dex premedication for CRS. The highest Dex concentrations caused ≤3-fold increases in the EC 50 of HPN217. Considering this and the plasma half-life of i.v. injected Dex at <5 h, the suppressive effect of Dex on the anti-tumor activity of HPN217-redirected T cells may be limited.
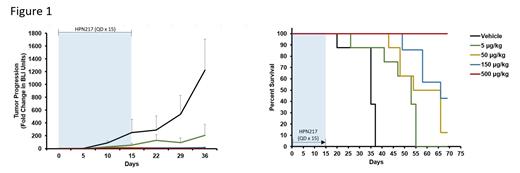
We then evaluated if MM.1S-Luc cell line xenografts in NCG mice would be a suitable model to extend the above in vitro findings to an in vivo setting. Lesions in the spine, skull and femur in NCG mice treated with vehicle could be detected by bioluminescent imaging. All mice succumbed to the disease within 40 days. By contrast, animals treated with HPN217 were protected in a dose-dependent manner. Mice that received the highest dose remained 100% disease-free at the end of the study (Figure 1).
Conclusions
We demonstrated HPN217 mediated BCMA-dependent primary MM cell killing by autologous T cells, and that the density of BCMA target on the surface of MM cells and sBCMA affected the efficacy of HPN217 in cultures. GSI, which increased the expression of BCMA on MM cells, enhanced the efficacy of HPN217. On the other hand, Dex had limited negative effect. HPN217 in combination with approved and experimental MM therapeutics is being evaluated in the 3DTEBM and MM.1S-Luc models.
Ng: Harpoon Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Aaron: Harpoon Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Callihan: Harpoon Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Hemmati: Harpoon Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Law: Harpoon Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Azab: Cellatrix, LLC: Current Employment, Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company. Sun: Harpoon Therapeutics: Consultancy, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Ended employment in the past 24 months.